
Mammographic breast density refines Tyrer-Cuzick estimates of breast cancer risk in high-risk women: findings from the placebo arm of the international breast cancer intervention study i. Breast Cancer Research 16 (5), 451+. UTSW CancerGene Software download. Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas and The BayesMendel Group CancerGene with BRCAPRO, MMRpro, PancPRO, and MelaPRO. Duke, JHU and UT Southwestern may terminate this Agreement immediately upon Licensee’s breach of this Agreement. Disclaimer of Warranties.
• 849 Downloads • Abstract Considerable differences exist amongst countries in the mutation probability methods and thresholds used to select patients for BRCA1/2 genetic screening. In order to assess the added value of mutation probability methods, we have retrospectively calculated the BRCAPRO and Myriad II probabilities in 306 probands who had previously been selected for DNA-analysis according to criteria based on familial history of cancer.
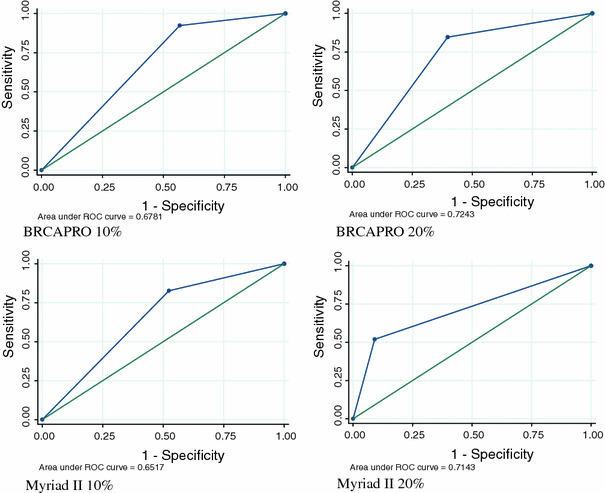
DNA-analysis identified 52 mutations (16.9%) and 11 unclassified variants (UVs, 3.6%). Compared to cancer history, a threshold ≥10% with BRCAPRO or with Myriad II excluded about 40% of the patients from analysis, including four with a mutation and probabilities 20% with BRCAPRO and Myriad II.
In summary, BRCAPRO and Myriad II are more efficient than cancer history alone to exclude patients without a mutation. BRCAPRO performs better for the detection of BRCA1 mutations than of BRCA2 mutations. The Myriad II scores provided no additional information than the BRCAPRO scores alone for the detection of patients with a mutation. Chertezhi dwg din 7982. The use of thresholds excluded from analysis the majority of patients carrying an UV.
The two major susceptibility genes for breast cancer (BC) and ovarian cancer (OC), BRCA1 (MIM: 113705) and BRCA2 (MIM: 600185 ) were discovered in 1994 and 1995, respectively [, ]. Initially, the Protein Truncation Test (PTT) was the screening method widely used as a quick and inexpensive test to detect pathogenic truncating mutations in these genes.
Mfps all addons for kodi. ULogin - MFPS 2. UMenu - MFPS 3. Ranking System - MFPS 4. Customizer Multiplayer - MFPS 5. Weapon PickUp Multiplayer - MFPS 6. Hud System - MFPS 7. Class Customization - MFPS 8. Kill Streak Notifier - MFPS 9. Level System - MFPS Description of all add-ons for MFPS. ULogin - MFPS Authorization system in MFPS. UMenu - MFPS New menu for MFPS.
At a later stage, the screening was optimised using denaturing high performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC) [ ], direct sequencing and Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA) [ ], in which all types of mutations or deletions could be detected. A drawback of this optimised screening methodology is that, as compared to PTT, it is laborious and more expensive. Furthermore, inherited mutations in these two genes only account for a small fraction of the familial clustering of BC and OC in the total group of index patients [,,,, ]. Therefore, accurate selection criteria for patients eligible for DNA-analysis are mandatory.
Various risk prediction algorithms and models have been developed to identify putative BRCA1/2 mutation carriers. The first published model was that of the University of Pennsylvania (U-Penn), also called the Couch model [ ]; followed by Shattuck-Eidens model or Myriad I [ ]; Myriad II, an extension of the previous model [ ]; the Myriad tables by Frank et al. [ ]; the BRCAPRO model [ ]; the Manchester scoring system of Evans et al. [ ] and the recent BOADICEA model of Antoniou et al. In addition to the different types of models, also the thresholds used in these models to establish the indication to perform DNA-analysis, vary substantially among countries. In 1996, the American Society of Clinical Oncology recommended that consideration of BRCA1/2 testing should be offered to patients with strong familial features, such as BC in the family or very early age at onset of the disease, c.q. Corresponding to those patients whose prior probability of carrying a mutation exceeds 10% [ ].
However, the updated American guidelines in 2003 did not recommend a numerical threshold [ ]. Currently, the majority of Dutch Cancer Genetics Services apply a 10% pre-test probability as threshold to perform DNA analysis of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes [ ], whereas in the UK most centres offer mutation analysis to families with a 20% or greater pre-test probability of carrying a mutation [ ]. The goal of our study was to retrospectively analyze the added value of predictive mutation probability scores and optimal thresholds in terms of sensitivity and specificity of two currently used mutation probability models BRCAPRO and Myriad II, in a group of patients prior selected on the basis of family history of cancer.

Materials and methods. BC Breast cancer, OC Ovarian cancer In the period 1996–2000 partial mutation screening of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes was performed using the protein truncation test (PTT). The PTT was used only for exon 11 of BRCA1 and exons 10 and 11 of BRCA2. From 2000 on, complete genetic screening was performed using DHPLC [ ], direct sequencing and for BRCA1 also MLPA [ ]. Clinical data of all the probands and their first and second degree relatives were retrieved from their medical records, which included cancer site: BC and/or OC, bilateral BC, BC in male relatives, age at diagnosis and number of affected relatives (data not shown). All probands were affected with breast cancer and/or ovarian cancer.
- Author: admin
- Category: Category

Mammographic breast density refines Tyrer-Cuzick estimates of breast cancer risk in high-risk women: findings from the placebo arm of the international breast cancer intervention study i. Breast Cancer Research 16 (5), 451+. UTSW CancerGene Software download. Southwestern Medical Center at Dallas and The BayesMendel Group CancerGene with BRCAPRO, MMRpro, PancPRO, and MelaPRO. Duke, JHU and UT Southwestern may terminate this Agreement immediately upon Licensee’s breach of this Agreement. Disclaimer of Warranties.
• 849 Downloads • Abstract Considerable differences exist amongst countries in the mutation probability methods and thresholds used to select patients for BRCA1/2 genetic screening. In order to assess the added value of mutation probability methods, we have retrospectively calculated the BRCAPRO and Myriad II probabilities in 306 probands who had previously been selected for DNA-analysis according to criteria based on familial history of cancer.
DNA-analysis identified 52 mutations (16.9%) and 11 unclassified variants (UVs, 3.6%). Compared to cancer history, a threshold ≥10% with BRCAPRO or with Myriad II excluded about 40% of the patients from analysis, including four with a mutation and probabilities 20% with BRCAPRO and Myriad II.
In summary, BRCAPRO and Myriad II are more efficient than cancer history alone to exclude patients without a mutation. BRCAPRO performs better for the detection of BRCA1 mutations than of BRCA2 mutations. The Myriad II scores provided no additional information than the BRCAPRO scores alone for the detection of patients with a mutation. Chertezhi dwg din 7982. The use of thresholds excluded from analysis the majority of patients carrying an UV.
The two major susceptibility genes for breast cancer (BC) and ovarian cancer (OC), BRCA1 (MIM: 113705) and BRCA2 (MIM: 600185 ) were discovered in 1994 and 1995, respectively [, ]. Initially, the Protein Truncation Test (PTT) was the screening method widely used as a quick and inexpensive test to detect pathogenic truncating mutations in these genes.
Mfps all addons for kodi. ULogin - MFPS 2. UMenu - MFPS 3. Ranking System - MFPS 4. Customizer Multiplayer - MFPS 5. Weapon PickUp Multiplayer - MFPS 6. Hud System - MFPS 7. Class Customization - MFPS 8. Kill Streak Notifier - MFPS 9. Level System - MFPS Description of all add-ons for MFPS. ULogin - MFPS Authorization system in MFPS. UMenu - MFPS New menu for MFPS.
At a later stage, the screening was optimised using denaturing high performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC) [ ], direct sequencing and Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA) [ ], in which all types of mutations or deletions could be detected. A drawback of this optimised screening methodology is that, as compared to PTT, it is laborious and more expensive. Furthermore, inherited mutations in these two genes only account for a small fraction of the familial clustering of BC and OC in the total group of index patients [,,,, ]. Therefore, accurate selection criteria for patients eligible for DNA-analysis are mandatory.
Various risk prediction algorithms and models have been developed to identify putative BRCA1/2 mutation carriers. The first published model was that of the University of Pennsylvania (U-Penn), also called the Couch model [ ]; followed by Shattuck-Eidens model or Myriad I [ ]; Myriad II, an extension of the previous model [ ]; the Myriad tables by Frank et al. [ ]; the BRCAPRO model [ ]; the Manchester scoring system of Evans et al. [ ] and the recent BOADICEA model of Antoniou et al. In addition to the different types of models, also the thresholds used in these models to establish the indication to perform DNA-analysis, vary substantially among countries. In 1996, the American Society of Clinical Oncology recommended that consideration of BRCA1/2 testing should be offered to patients with strong familial features, such as BC in the family or very early age at onset of the disease, c.q. Corresponding to those patients whose prior probability of carrying a mutation exceeds 10% [ ].
However, the updated American guidelines in 2003 did not recommend a numerical threshold [ ]. Currently, the majority of Dutch Cancer Genetics Services apply a 10% pre-test probability as threshold to perform DNA analysis of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes [ ], whereas in the UK most centres offer mutation analysis to families with a 20% or greater pre-test probability of carrying a mutation [ ]. The goal of our study was to retrospectively analyze the added value of predictive mutation probability scores and optimal thresholds in terms of sensitivity and specificity of two currently used mutation probability models BRCAPRO and Myriad II, in a group of patients prior selected on the basis of family history of cancer.

Materials and methods. BC Breast cancer, OC Ovarian cancer In the period 1996–2000 partial mutation screening of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes was performed using the protein truncation test (PTT). The PTT was used only for exon 11 of BRCA1 and exons 10 and 11 of BRCA2. From 2000 on, complete genetic screening was performed using DHPLC [ ], direct sequencing and for BRCA1 also MLPA [ ]. Clinical data of all the probands and their first and second degree relatives were retrieved from their medical records, which included cancer site: BC and/or OC, bilateral BC, BC in male relatives, age at diagnosis and number of affected relatives (data not shown). All probands were affected with breast cancer and/or ovarian cancer.